Keeping up with Google's algorithms is a full-time job. In the past year it's cracked down on ad-heavy content (Fred), shaken up local search results (Possum), and completely changed how websites are indexed (mobile-first indexing).
If you forgot to tend to your technical SEO while you were busy surviving Google algorithm updates, I could hardly blame you. Fortunately, there's no time like the present to double-check your site health and conduct an SEO audit.
This checklist will run you through all the technical SEO fundamentals you need in place in the year ahead.
1. Install essential tools
Your ability to improve your SEO hinges on your tools' ability to find and fix technical problems. Here are the absolute essentials you'll need:
- Google Analytics: Track website traffic and gain insight into your visitors.
- Google Search Console: Measure site performance and errors. If you're targeting US markets, you might also want to sign up for Bing Webmaster Tools.
- Yoast SEO plugin (if you're using WordPress): Optimize your content, metadata, sitemap, keywords, and more(must have for WordPress sites).
- An SEO auditing tool: I'll be using my tool, WebSite Auditor.
Those tools are the absolute bare minimum for improving your technical SEO.
You won't need anything else to follow along in this article, but if you feel you've reached your limit with Google's free tools and you want to step up your SEO game, I highly recommend you consider tools that will let you dig deeper into your analytics. There are a ton of options, so you're sure to find something that suits your needs.
Consider your needs and your budget, and then look for software that lets you...
- Monitor your link health, find and fix broken links, and discover new link-building opportunities.
- Correct more errors, such as 404/500 error pages, faulty redirects, W3C validation errors, etc.
- Perform deeper keyword analysis and optimize for all rankings, including local and geo-specific.
- Discover content errors such as thin content, duplicate content, canonicalization errors, etc.
- Spy on your competitors and compare backlinks, anchor text, etc.
2. Improve indexing and crawlability
One of the best ways to find out whether your site has too many duplicate URLs, noncanonical URLs, and URLs that contain a noindex metatag is to check your index status.
To do this, enter site:yourdomain.com into your target search engine, use your favorite SEO crawling software, or log in to Google Search Console and click Google Index > Index Status to see your report.
Ideally, you want your total indexed pages as close to your total number of pages as possible.
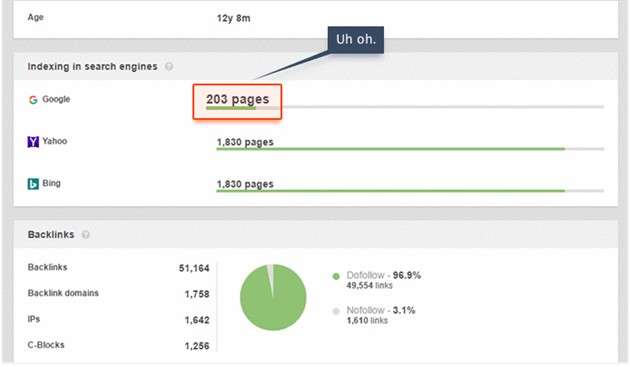
Note that while manually reviewing your robots.txt will help you discover some disallowed pages, you're liable to miss many others. I recommend a more dedicated tool that will help you find all blocked pages, including those blocked by robots.txt instructions, noindex metatags, and X-Robot-Tag headers.
3. Improve your 'crawl budget'
We call the number of pages on your website that search engine spiders crawl in a given period of time your "crawl budget." You probably won't have to worry about crawl budget (unless your site is gigantic), but working to improve your crawl budget almost always translates into improving your technical SEO.
To view your approximate crawl budget, log in to Google Search Console and click Crawl > Crawl Stats. Unfortunately, finding a page-by-page breakdown of your crawl stats is a little harder and will require a separate tool.
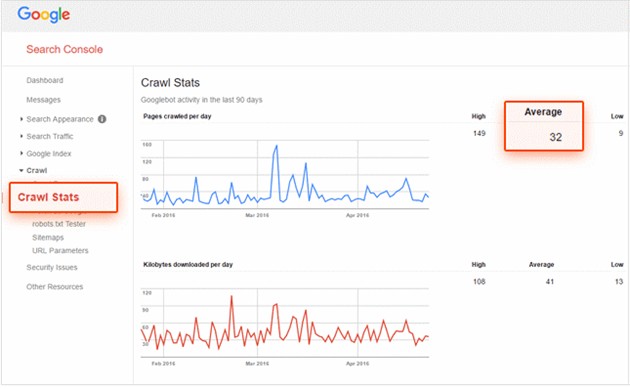
My team recently tested whether it's possible to boost your crawl budget. What we found is a strong correlation between the number of spider hits and external links, which suggests that growing your link profile will also improve your crawl budget.
Building links organically takes time, however. If you want to improve your crawl budget right now while you begin grooming your link profile, I suggest auditing your internal links, fixing broken links, and limiting your use of uncrawlable media-rich files.
Revisiting your URL structure will also improve your crawl budget. Ensure that all of your URLs are as succinct as possible, include 1-2 focused keywords, and easily identify the topic. For example, if this article's URL were "marketingprofs.com/410571591," we might change it to "marketingprofs.com/2018-technical-seo-checklist."
(For more advice, check out this guide to improving your crawl budget.)
4. Clean up your sitemap
You can also boost your crawlability by improving your sitemap navigation. You can check your sitemap for errors by clicking Crawl > Sitemaps in your Google Search Console.
For the sake of technical SEO, you'll want to make sure that your XML sitemap is...
- Not too large: Google limits a single sitemap to 10MB (uncompressed) and 50,000 URLs. If you exceed those limits, break your site into multiple sitemaps or create a sitemap index file and submit it to Google.
- Up to date: Whenever you add content to your site, update your XML sitemap and submit it to Google.
- Uncluttered: Remove all noncanonical URLs, redirects, 400-level pages, and blocked pages from your sitemap.
While you're optimizing your XML sitemap for search engines, don't forget to update your HTML sitemaps, too. Doing so will help improve user experience for your site visitors.
5. Optimize metadata
Review your HTML code and improve your meta descriptions and title tags wherever they're missing. Here are some general guidelines you can follow:
Title Tags
- The length should be 70-71 characters for desktop, 78 characters for mobile.
- Accurately reflect the content on your page.
- Lead with your most important keywords, but don't keyword-stuff your title tags.
- Insert your brand/company name at the end of your title tags.
- Don't duplicate title tags across multiple pages.
- Make it different from your H1 headline.
Meta Descriptions
- The length should be 200 characters for desktop, 170-172 characters for mobile.
- They should be a brief, readable, and unique description of a page's topic.
- Naturally insert 1-2 keywords consistent with title tag keywords.
Headline Tags
- Tag your main headline with an H1 tag (only one H1 tag per page!).
- Use H2 tags for sub-headers or different topics on the same page.
- If you use sub-headers within your sub-headers (lists, source links, etc.) use more H3–H6 tags, in descending order.
6. Fix broken links and redirects
After you've performed your website audit, fixing any redirect chains and broken links is among the best bits of technical SEO you can perform. Redirects and broken links eat up valuable crawl budget, slow down your page, result in a poorer user experience, and may ultimately devalue your page. It's in your best interest to fix them ASAP.
Broken Links
Broken internal links are easy enough to fix: Just find the offending page and turn the broken link into a link to an existing page. Try to keep your site structure as shallow as possible so that no page is more than three clicks away from your homepage.
To fix broken external links, you'll have to contact the webmaster and ask them to fix or remove your link. If that's not possible, you may have to set up a 301 redirect to an active page or disavow the dead link (especially if it's from an unreputable source).
Redirect Chains
Fix chains of three or more redirects first, and do what you can to eliminate redirects altogether. Having many redirects in a row might result in search engine spiders' dropping off before they reach the end of the chain, which might result in unindexed pages.
Orphan Pages
You may also discover orphan pages during your SEO audit. These are pages that aren't linked to from any other page of your website. Add links to ensure that visitors and search engines can find that page.
7. Use rich snippets and structured data
Schema markup gives users a snapshot of your content before they click on the page so that they can see thumbnail images, star ratings, and additional product details before clicking on your link.

Rich snippets like this help build consumer trust and often encourage clickthroughs.
Go to Schema.org to learn how to set up structured data for your pages, then use Google's Structured Data Testing Tool to review your snippets.
8. Optimize site speed for mobile
A recent Google study found that visitors are three times more likely to abandon a page with a 1-5-second load time than bounce from a page with a 1-3-second load time.
Site speed has always been one of Google's most important ranking signals, and it's one of the most important technical SEO elements related to your conversions as well.
Unfortunately, slow load times are common, especially on mobile sites. Google's study noted that "the majority of mobile websites are slow and bloated with too many elements," and 70% of pages took nearly seven seconds to load their above-the-fold content.
Here's what you can do to improve your site speed and mobile performance:
- Run your page through Google's free tools, including PageSpeed Insights, Mobile-Friendly Test, and Test My Site. Make the changes they recommend.
- Optimize your images.
- Minify JavaScript and CSS Files.
- Move files such as images, CSS, and Javascript to a CDN (content delivery network).
If you're looking for technical SEO to improve on your page, this is a good place to start. With Google's recent switch to mobile-first indexing, your site ranking will be largely determined by your mobile site's performance.
9. Look to the future (voice search, RankBrain, and more)
Checklists like this are great if you've fallen behind on your technical SEO, but they don't often help you prepare for upcoming trends. So do yourself a favor and brush up on other innovations you can use to solve customer pain points, such as...
- Voice search: Local businesses are becoming increasingly discovered via voice chat, through queries such as "I want to buy _____" or "What are _____ businesses near me?" Optimize for voice search to help these customers find you.
- RankBrain/AI: RankBrain allows Google to understand what would be the best result for the user's query, based on historical data. The algorithm is focused on quality for the end-user, so optimize the experience for the audience that you want coming to your website.
- Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP), mobile apps, and progressive Web apps (PWA): As mobile usage increases and Google shifts toward mobile-first indexing, developers are working hard to make the mobile Web as efficient and useful as possible.
* * *
Studies show that after performing a major site audit, 39% of SEOs tackle technical SEO first. Improving your technical SEO is great, because it gives you a bedrock upon which to build everything else, but don't forget about other SEO elements in the process.
At the end of the day, you still need great content, you still need to build citations in prominent directories, and you still need to build up a strong social media presence.
Make sure every part of your website is working together to establish you as an authority in your niche and improve your Web presence.




